For many companies, assessing and reducing their environmental footprint has become a major concern, and Data4 is no exception.
The Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol has become one of the most important tools for achieving these objectives. The GHG Protocol’s methodological framework allows companies to measure, manage, and reduce their greenhouse gas emissions in a rigorous and transparent way, which is essential for working toward carbon neutrality. Data4, through its Data4Good program, pursues its environmental commitments by putting sustainability at the heart of its strategy.
A protocol for identifying pollution sources
Developed in the late 1990s by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), the GHG Protocol provides a standardized methodology for GHG emissions accounting and management. It helps companies understand and reduce their environmental impact.
Data4 uses this methodology when preparing its GHG emissions inventory, ensuring that its business activities are well aligned with its sustainability goals.
The importance of the GHG Protocol lies in its ability to offer a consistent approach for measuring CO2 emissions, which is essential for assessing an organization’s carbon footprint. Data4 uses the protocol to identify its main sources of pollution, making it easier to reduce emissions and improve energy management practices.
For companies, GHG emissions accounting is a key element of their sustainability strategies. Every year, Data4 measures its emissions for each of the three scopes in each country where it operates. An accurate assessment of the company’s carbon footprint helps Data4 not only comply with environmental regulations, but also meet the growing expectations of different stakeholders in terms of social and environmental responsibility.
The GHG Protocol divides GHG emissions into three categories, or “scopes,” covering all emissions linked to a company’s activities. This classification is crucial for understanding the breakdown of the different sources of CO2 emissions, including both direct emissions and indirect emissions. By adopting this framework, Data4 can develop emission-reduction strategies tailored to its specific needs while contributing to the fight against global warming.
Emissions inventory: Definition & objectives
A GHG emissions inventory is a method of assessing a company’s carbon footprint by accounting for all the GHG emissions generated directly or indirectly by its activities. Data4 uses the GHG Protocol to measure these emissions, covering all three scopes, enabling the company to identify opportunities for improvement to reduce its emissions and improve the sustainability of its activities.
The main aim of the emissions inventory is to reduce GHG emissions. Data4, as part of its commitment to the Climate Neutral Data Center Pact, strives not only to measure its emissions, but also to implement appropriate action plans to reduce them. In addition, to cover its residual emissions, Data4 invests in carbon sinks, thus contributing to the goal of carbon neutrality in its ecosystem.
A closer look at the 3 scopes
Scope 1
GHG emissions are sorted into different categories to facilitate their management and reduction. Scope 1 corresponds to direct emissions, i.e., emissions from sources directly controlled by the company.
Direct emissions
Direct emissions include all GHGs emitted by activities under the direct control of the company, such as the operation of electrical generators, refrigeration systems, and company cars.
Scope 2
In addition to direct emissions, companies must also take into account indirect energy-related emissions, labeled “scope 2.” These emissions are generated by the production of the energy the company purchases to power its operations.
Indirect emissions tied to energy
Scope 2 covers indirect emissions resulting from the consumption of electricity, heat, or steam purchased by the company. Data4 pays special attention to these emissions, given that its activities require significant energy consumption. To reduce the impact of these emissions, in March 2024, Data4 signed two major contracts with French leaders in renewable energy: Eurowatt and Photosol. Under these contracts, known as power purchase agreements (PPAs), the two energy providers will supply decarbonized energy to Data4, responding to the rapid growth of the digital sector and the growing importance of environmental responsibility.
Scope 3
Scope 3 covers indirect emissions not included in scope 2. These emissions come from activities which are not directly controlled by the company, but which are nevertheless linked to its value chain.
Indirect emissions in the value chain
Scope 3 emissions include a wide range of indirect activities, such as emissions linked to the production of purchased goods and services, the transportation of goods, and waste management. Data4 recognizes that this scope often represents the largest source of GHG emissions for a company, and therefore focuses on measuring and reducing them.
Categories of scope 3
Scope 3 emissions are divided into upstream emissions and downstream emissions. Data4 takes into account a wide range of emissions categories, from those tied to the construction of its new data centers to those resulting from waste management on its various campuses.
The 3 scopes for Data4
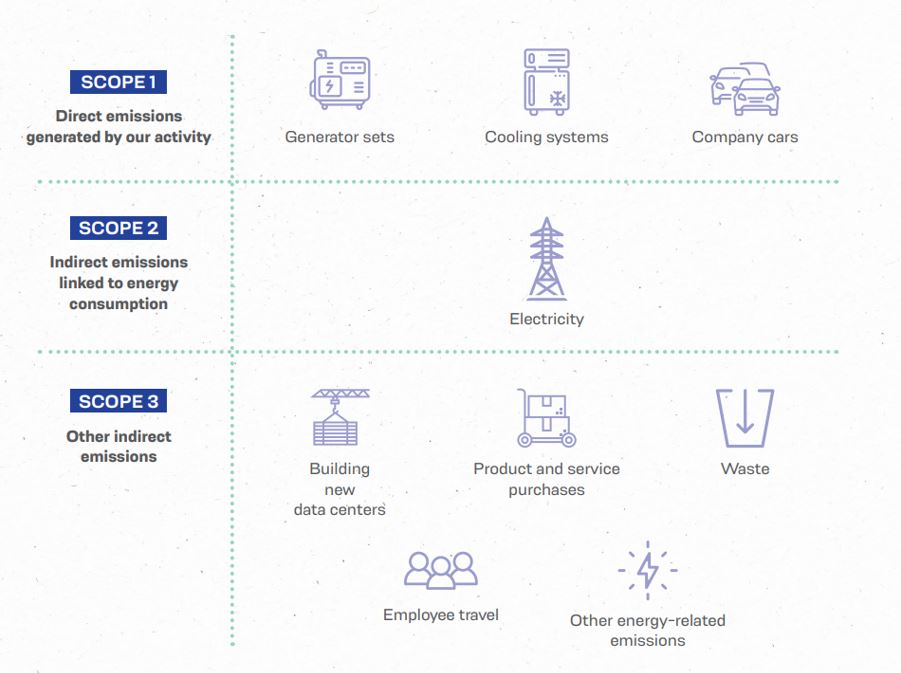
Why it’s important to distinguish between scopes 1, 2, and 3
The distinction between scopes 1, 2, and 3 of emissions is crucial for effectively managing GHG emissions. Doing so helps companies better understand the different sources of their emissions and develop targeted strategies to reduce them.
Emissions management
To manage and reduce GHG emissions, companies like Data4 need to identify and understand the sources of emissions in each of the three scopes. From there, they can implement specific actions to reduce their direct emissions (scope 1), improve energy efficiency (scope 2), and work with value chain partners to reduce indirect emissions (scope 3).
Reporting and transparency
GHG emissions reporting is a key element for companies’ transparency about their sustainability. Data4 is committed to publishing detailed reports on its emissions, demonstrating its commitment to carbon emissions reductions and the company’s contribution to the fight against global warming.
In short, the GHG Protocol is an essential tool for understanding and managing emissions across scopes 1, 2, and 3. By accurately measuring their carbon footprints, companies like Data4 can not only reduce their GHG emissions, but also reinforce their commitment to sustainability.

